
HL Paper 1
Which type of bond is formed when a Lewis acid reacts with a Lewis base?
A. Covalent
B. Dipole-dipole
C. Double
D. Hydrogen
Which compounds can be mixed together as solutions of equal volume and concentration to form a buffer solution?
A. Nitric acid and potassium hydroxide
B. Nitric acid and potassium nitrate
C. Propanoic acid and potassium hydroxide
D. Propanoic acid and potassium propanoate
Which salt solution has the highest pH?
A. NH4Cl
B. Ca(NO3)2
C. Na2CO3
D. K2SO4
The graph below shows the titration curve of \({\text{25 c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}}\) of \({\text{0.100 mol}}\,{\text{d}}{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}\) of hydrochloric acid with sodium hydroxide, of \({\text{0.100 mol}}\,{\text{d}}{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}\) concentration. The indicator methyl orange was used to determine the equivalence point. Methyl orange has a pH range of 3.2– 4.4.
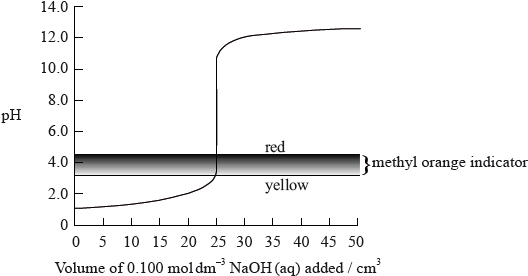
If the hydrochloric acid was replaced by ethanoic acid of the same volume and concentration, which property of the titration would remain the same?
A. The initial pH
B. The pH at the equivalence point
C. The volume of strong base, NaOH, needed to reach the equivalence point
D. The colour of the titration mixture just before the equivalence point is reached
For which equilibrium can an expression for a base dissociation constant, \({K_{\text{b}}}\), for the forward reaction be written?
A. \({\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_3} + {{\text{H}}_3}{{\text{O}}^ + } \rightleftharpoons {\text{NH}}_4^ + + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}\)
B. \({{\text{F}}^ - } + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}} \rightleftharpoons {\text{HF}} + {\text{O}}{{\text{H}}^ - }\)
C. \({\text{NH}}_4^ + + {\text{O}}{{\text{H}}^ - } \rightleftharpoons {\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_3} + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}\)
D. \({\text{HF}} + {\text{O}}{{\text{H}}^ - } \rightleftharpoons {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}} + {{\text{F}}^ - }\)
Which statements are correct?
I. Lewis bases can act as nucleophiles.
II. Electrophiles are Lewis acids.
III. Lewis acids are electron pair acceptors.
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
Which combination of acid and base is most likely to have a pH of 8.5 at the equivalence point in a titration?
A. Hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide
B. Hydrochloric acid and ammonia
C. Nitric acid and ammonia
D. Methanoic acid and sodium hydroxide
Which definition of a base is correct?
A. A Lewis base accepts a proton.
B. A Brønsted-Lowry base accepts an electron pair.
C. A Brønsted-Lowry base donates an electron pair.
D. A Lewis base donates an electron pair.
The \({K_{\text{b}}}\) value for a base is \(5.0 \times {10^{ - 2}}{\text{ mol}}\,{\text{d}}{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}\) at 298 K. What is the \({K_{\text{a}}}\) value for its conjugate acid at this temperature?
A. \(5.0 \times {10^{ - 2}}\)
B. \(2.0 \times {10^{ - 6}}\)
C. \(2.0 \times {10^{ - 12}}\)
D. \(2.0 \times {10^{ - 13}}\)
The colours of three indicators are shown in the table below.
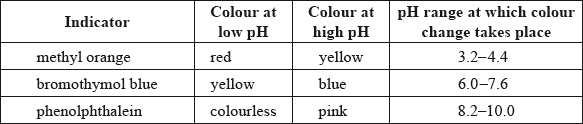
Equal volumes of these three indicators were mixed and the mixture was added to a solution of \({\text{pH}} = 5.0\). What colour would be seen?
A. Yellow
B. Orange
C. Green
D. Blue
What is the expression for the ionic product constant of water, \({K_{\text{w}}}\)?
A. \({K_{\text{w}}} = {K_{\text{a}}} \times {K_{\text{b}}}\)
B. \({K_{\text{w}}} = {K_{\text{a}}} + {K_{\text{b}}}\)
C. \({K_{\text{w}}} = \frac{{{K_{\text{a}}}}}{{{K_{\text{b}}}}}\)
D. \({K_{\text{w}}} = {K_{\text{a}}} - {K_{\text{b}}}\)
The indicator, HIn is used in a titration between an acid and base. Which statement about the dissociation of the indicator, HIn is correct?
\[{\text{HIn(aq)}} \rightleftharpoons {{\text{H}}^ + }{\text{(aq)}} + {\text{I}}{{\text{n}}^ - }{\text{(aq)}}\]
colour A colour B
A. In a strongly alkaline solution, colour B would be observed.
B. In a strongly acidic solution, colour B would be observed.
C. \({\text{[I}}{{\text{n}}^ - }{\text{]}}\) is greater than [HIn] at the equivalence point.
D. In a weakly acidic solution colour B would be observed.
The \({K_{\text{a}}}\) values of four weak acids W, X, Y and Z are listed below.
W \({K_{\text{a}}} = 1.35 \times {10^{ - 3}}\)
X \({K_{\text{a}}} = 4.47 \times {10^{ - 2}}\)
Y \({K_{\text{a}}} = 9.33 \times {10^{ - 6}}\)
Z \({K_{\text{a}}} = 1.47 \times {10^{ - 5}}\)
The acid–base indicator phenol red, HIn, changes colour from yellow to red over a pH range of 6.6–8.2. Which statement is correct?
A. In a strongly acidic solution \({\text{[HIn]}} < {\text{[I}}{{\text{n}}^ - }{\text{]}}\).
B. The \({\text{p}}{K_{\text{a}}}\) of phenol red is between 6.6 and 8.2.
C. The \({\text{I}}{{\text{n}}^ - }\) ions are yellow.
D. Phenol red would be a suitable indicator for the titration of a strong acid and a weak base.
Methylamine acts as a weak base when it reacts with water. For a diluted aqueous solution, what is the \({K_{\text{b}}}\) expression for this reaction?
A. \({K_{\text{b}}} = \frac{{{\text{[C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{NH}}_{\text{3}}^ + {\text{][O}}{{\text{H}}^ - }{\text{]}}}}{{{\text{[C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{]}}}}\)
B. \({K_{\text{b}}} = \frac{{{\text{[C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{][}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O]}}}}{{{\text{[C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{NH}}_{\text{3}}^ + {\text{][O}}{{\text{H}}^ - }{\text{]}}}}\)
C. \({K_{\text{b}}} = \frac{{{\text{[C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{NH}}_{\text{3}}^ + {\text{][O}}{{\text{H}}^ - }{\text{]}}}}{{{\text{[C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{][}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O]}}}}\)
D. \({K_{\text{b}}} = \frac{{{\text{[C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{]}}}}{{{\text{[C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{NH}}_{\text{3}}^ + {\text{][O}}{{\text{H}}^ - }{\text{]}}}}\)
Four aqueous solutions are listed below.
W. \({\text{0.100 mol}}\,{\text{d}}{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}{\text{ HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{(aq)}}\)
X. \({\text{0.001 mol}}\,{\text{d}}{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}{\text{ HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{(aq)}}\)
Y. \({\text{0.100 mol}}\,{\text{d}}{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}{\text{ KOH(aq)}}\)
Z. \({\text{0.001 mol}}\,{\text{d}}{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}{\text{ KOH(aq)}}\)
What is the correct order of increasing pH of these solutions?
A. \({\text{W}} < {\text{X}} < {\text{Y}} < {\text{Z}}\)
B. \({\text{W}} < {\text{X}} < {\text{Z}} < {\text{Y}}\)
C. \({\text{X}} < {\text{W}} < {\text{Y}} < {\text{Z}}\)
D. \({\text{X}} < {\text{W}} < {\text{Z}} < {\text{Y}}\)
Which of the following is an example of a Lewis acid–base reaction, but not a Brønsted–Lowry acid–base reaction?
A. \({\text{2CrO}}_4^{2 - }{\text{(aq)}} + {\text{2}}{{\text{H}}^ + }{\text{(aq)}} \to {\text{C}}{{\text{r}}_2}{\text{O}}_7^{2 - }{\text{(aq)}} + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O(l)}}\)
B. \({\text{Co(}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O)}}_6^{2 + }{\text{(aq)}} + {\text{4HCl(aq)}} \to {\text{CoCl}}_4^{2 - }{\text{(aq)}} + {\text{4}}{{\text{H}}^ + }{\text{(aq)}} + {\text{6}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O(l)}}\)
C. \({\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{(aq)}} + {{\text{H}}^ + }{\text{(aq)}} \to {\text{NH}}_4^ + {\text{(aq)}}\)
D. \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{CO}}{{\text{O}}^ - }{\text{(aq)}} + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O(l)}} \to {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{COOH(aq)}} + {\text{O}}{{\text{H}}^ - }{\text{(aq)}}\)
Which equation represents a reaction for which a base dissociation constant expression, \({K_b}\), can be written?
A. \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{COOH(aq)}} + {\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{(aq)}} \rightleftharpoons {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CO}}{{\text{O}}^ - }{\text{(aq)}} + {\text{NH}}_4^ + {\text{(aq)}}\)
B. \({\text{HF(aq)}} \rightleftharpoons {{\text{H}}^ + }{\text{(aq)}} + {{\text{F}}^ - }{\text{(aq)}}\)
C. \({\text{HCN(aq)}} + {\text{O}}{{\text{H}}^ - }{\text{(aq)}} \rightleftharpoons {\text{C}}{{\text{N}}^ - }{\text{(aq)}} + {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O(l)}}\)
D. \({\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{(aq)}} + {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O(l)}} \rightleftharpoons {\text{NH}}_4^ + {\text{(aq)}} + {\text{O}}{{\text{H}}^ - }{\text{(aq)}}\)
A weak acid is titrated with a strong base. Which statement is true for the titration curve?
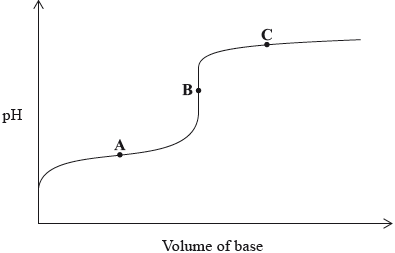
A. A is the equivalence point.
B. The pH at A equals the \({\text{p}}{K_{\text{a}}}\) of the acid.
C. The pH at B equals 7.
D. C is in the buffer region.
Which mixture will form a buffer in aqueous solution?
A. \({\text{0.10 mol N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}} + {\text{0.20 mol HCl}}\)
B. \({\text{0.10 mol N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}} + {\text{0.20 mol NaOH}}\)
C. \({\text{0.10 mol NaOH}} + {\text{0.20 mol KCl}}\)
D. \({\text{0.20 mol N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}} + {\text{0.10 mol HCl}}\)
Ammonia acts as a weak base when it reacts with water. What is the \({K_{\text{b}}}\) expression for this reaction?
A. \(\frac{{[{\text{NH}}_4^ + ][{\text{O}}{{\text{H}}^ - }]}}{{[{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_3}][{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O]}}}}\)
B. \(\frac{{[{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{][}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O]}}}}{{{\text{[NH}}_4^ + {\text{][O}}{{\text{H}}^ - }{\text{]}}}}\)
C. \(\frac{{[{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_3}]}}{{[{\text{NH}}_4^ + ][{\text{O}}{{\text{H}}^ - }]}}\)
D. \(\frac{{[{\text{NH}}_4^ + ][{\text{O}}{{\text{H}}^ - }]}}{{[{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_3}]}}\)
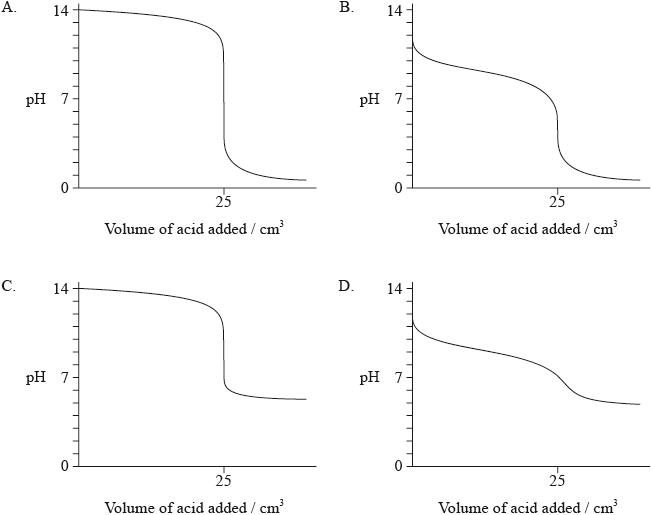
Which titration curve is produced by the titration of \({\text{25 c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}}\) of \({\text{1.00 mol}}\,{\text{d}}{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}\) NaOH with \({\text{1.00 mol}}\,{\text{d}}{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}{\text{ C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{COOH}}\)?
Which reaction represents an acid–base reaction according to the Lewis theory but not according to the Brønsted–Lowry theory?
A. \({\text{CO}}_3^{2 - }({\text{aq)}} + {{\text{H}}_3}{{\text{O}}^ + }({\text{aq)}} \rightleftharpoons {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O(l)}} + {\text{HCO}}_3^ - {\text{(aq)}}\)
B. \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{COOH(aq)}} + {\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_3}({\text{aq)}} \rightleftharpoons {\text{NH}}_4^ + ({\text{aq)}} + {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{CO}}{{\text{O}}^ - }({\text{aq)}}\)
C. \({\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_3}({\text{aq)}} + {\text{HF(aq)}} \rightleftharpoons {\text{NH}}_4^ + ({\text{aq)}} + {{\text{F}}^ - }({\text{aq)}}\)
D. \({\rm{CuS}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{4}}}{\rm{(s)}} + 5{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{O(l)}} \rightleftharpoons {\rm{CuS}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{4}}}{\rm{ \bullet 5}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{O(s)}}\)
Which is an example of a Lewis base?
A. an electrophile
B. BF3
C. CH4
D. a nucleophile
Which mixtures could act as buffers?
I. NaOH(aq) and HCl(aq)
II. NaOH(aq) and \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{COOH(aq)}}\)
III. HCl(aq) and \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{COONa(aq)}}\)
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
At the same concentration, which acid would have the lowest pH?
\(\begin{array}{*{20}{l}} {{\text{A.}}}&{{\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}}&{{K_{\text{a}}} = 5.6 \times {{10}^{ - 4}}{\text{ mol}}\,{\text{d}}{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}} \\ {{\text{B.}}}&{{\text{HF}}}&{{K_{\text{a}}} = 6.8 \times {{10}^{ - 4}}{\text{ mol}}\,{\text{d}}{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}} \\ {{\text{C.}}}&{{{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{COOH}}}&{{K_{\text{a}}} = 6.3 \times {{10}^{ - 5}}{\text{ mol}}\,{\text{d}}{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}} \\ {{\text{D.}}}&{{\text{HCN}}}&{{K_{\text{a}}} = 4.9 \times {{10}^{ - 10}}{\text{ mol}}\,{\text{d}}{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}} \end{array}\)
Consider the equation for the dissociation of water:
\[\begin{array}{*{20}{l}} {{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O(l)}} \rightleftharpoons {{\text{H}}^ + }{\text{(aq)}} + {\text{O}}{{\text{H}}^ - }{\text{(aq)}}}&{\Delta H = + 57.3{\text{ kJ}}\,{\text{mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ - 1}}} \end{array}\]
Which statement is correct?
A. The pH of pure water is always 7.
B. At temperatures above 298 K the pH of pure water is below 7.
C. At temperatures above 298 K the pH of pure water is above 7.
D. \({K_{\text{w}}}\) decreases with increasing temperature.
Which pair of compounds could be used to make a buffer solution (assuming appropriate molar ratios)?
A. KCl and HCl
B. NaCl and HCl
C. \({\text{KHS}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\) and \({{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\)
D. \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{COONa}}\) and \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{COOH}}\)
During a titration, \({\text{0.1 mol}}\,{\text{d}}{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}\) sodium hydroxide is added to \({\text{0.1 mol}}\,{\text{d}}{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}\) ethanoic acid. Which indicator would be the best to use as an end point indicator in this titration?
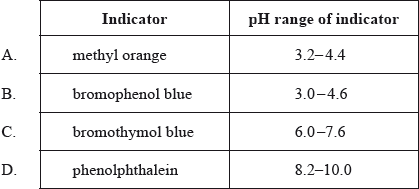
Bromophenol blue changes from yellow to blue over the pH range of 3.0 to 4.6. Which statement is correct?
A. Molecules of bromophenol blue, HIn, are blue.
B. At \({\text{pH}} < 3.0\), a solution of bromophenol blue contains more ions, \({\text{I}}{{\text{n}}^ - }\), than molecules, HIn.
C. The \({\text{p}}{K_{\text{a}}}\) of bromophenol blue is between 3.0 and 4.6.
D. Bromophenol blue is a suitable indicator to titrate ethanoic acid with potassium hydroxide
solution.
\({\text{100 c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}}\) of a NaOH solution of pH 12 is mixed with \({\text{900 c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}}\) of water. What is the pH of the resulting solution?
A. 1
B. 3
C. 11
D. 13
B. The aluminium atoms behave as Lewis bases.
C. One aluminium atom is a Lewis base and the other a Lewis acid.
D. One chlorine atom is a Lewis base and the other a Lewis acid.
Equal volumes and concentrations of hydrochloric acid and ethanoic acid are titrated with sodium hydroxide solutions of the same concentration. Which statement is correct?
A. The initial pH values of both acids are equal.
B. At the equivalence points, the solutions of both titrations have pH values of 7.
C. The same volume of sodium hydroxide is needed to reach the equivalence point.
D. The pH values of both acids increase equally until the equivalence points are reached.
Which statements are correct about the complex \({\text{[Cu(N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{]}}\)?
I. Oxidation state of copper is +2.
II. Ammonia is a ligand.
III. Chloride ions act as Lewis acids.
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
In which reaction does \({{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}\) act as a Lewis base but not as a Brønsted–Lowry base.
A. \({{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}} + {\text{NH}}_4^ + \to {{\text{H}}_3}{{\text{O}}^ + } + {\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_3}\)
B. \({{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}} + {\text{CaO}} \to {\text{C}}{{\text{a}}^{{\text{2}} + }} + {\text{2O}}{{\text{H}}^ - }\)
C. \({{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}} + {{\text{[Fe(}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}{{\text{)}}_6}{\text{]}}^{{\text{3}} + }} \to {\text{Fe[(OH)(}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}{{\text{)}}_5}{{\text{]}}^{{\text{2}} + }} + {{\text{H}}_3}{{\text{O}}^ + }\)
D. \({\text{6}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}} + {{\text{[Ni(N}}{{\text{H}}_3}{{\text{)}}_6}{\text{]}}^{2 + }} \to {\text{6N}}{{\text{H}}_3} + {{\text{[Ni(}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}{{\text{)}}_6}{\text{]}}^{2 + }}\)
The strengths of four acids are:
glycine \({\text{p}}{K_{\text{a}}} = {\text{9.87}}\)
chloroethanoic acid \({K_{\text{a}}} = 1.38 \times {10^{ - 3}}\)
phenol \({K_{\text{a}}} = 1.00 \times {10^{ - 10}}\)
butanoic acid \({\text{p}}{K_{\text{a}}} = 4.82\)
What is the order of increasing acid strength?
A. \({\text{chloroethanoic acid}} < {\text{butanoic acid}} < {\text{phenol}} < {\text{glycine}}\)
B. \({\text{glycine}} < {\text{phenol}} < {\text{chloroethanoic acid}} < {\text{butanoic acid}}\)
C. \({\text{phenol}} < {\text{chloroethanoic acid}} < {\text{butanoic acid}} < {\text{glycine}}\)
D. \({\text{phenol}} < {\text{glycine}} < {\text{butanoic acid}} < {\text{chloroethanoic acid}}\)
Based on information in the table below, which acid is the strongest?
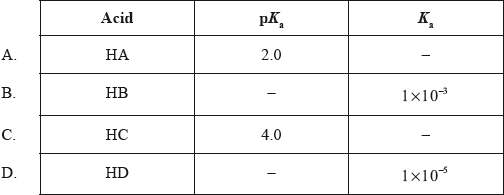
Methyl orange is an indicator which changes its colour from red to yellow in a pH range of 3.2 – 4.4.
For which titration would methyl orange be a suitable indicator?
A. Iodine and sodium thiosulfate solution
B. Hydrochloric acid and ammonia solution
C. Ethanoic acid and sodium hydroxide solution
D. Ethanoic acid and ammonia solution
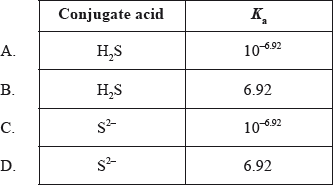
The \({\text{p}}{K_{\text{b}}}\) of \({\text{H}}{{\text{S}}^ - }\) is 7.08. What is its conjugate acid and what is the \({K_{\text{a}}}\) value of the acid?
Cobalt forms the complex \({{\text{[Co(N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{)}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{Cl]}}^{2 + }}\). Which statements are correct for this complex?
I. The cobalt ion acts as a Lewis acid.
II. The cobalt ion has an oxidation number of +II.
III. There are 90° bond angles between the cobalt ion and the ligands.
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
Which of the following will form a buffer solution if combined in appropriate molar ratios?
A. HCl and NaCl
B. NaOH and HCOONa
C. NH4Cl and HCl
D. HCl and NH3
Which mixtures are buffer solutions?
I. \({\text{KHS}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}{\text{(aq)}}\) and \({{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}{\text{(aq)}}\)
II. \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{COONa(aq)}}\) and \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{COOH(aq)}}\)
III. \({\text{HCOOK(aq)}}\) and \({\text{HCOOH(aq)}}\)
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
For which titration can the end point not be determined accurately by using an acid-base indicator?
A. \({\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{(aq)}} + {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{COOH(aq)}}\)
B. \({\text{NaOH(aq)}} + {\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{(aq)}}\)
C. \({\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{(aq)}} + {\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{(aq)}}\)
D. \({\text{NaOH(aq)}} + {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{COOH(aq)}}\)
The table below shows data for the \({{K_{\text{a}}}}\) and \({{\text{p}}{K_{\text{b}}}}\) values for some acids and bases at 298 K.
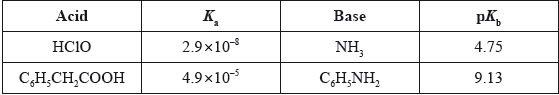
Which two formulas represent the weakest acid and the weakest base in the table?
A. HClO and \({{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\)
B. \({{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{COOH}}\) and \({\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\)
C. \({{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{COOH}}\) and \({{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\)
D. HClO and \({\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\)
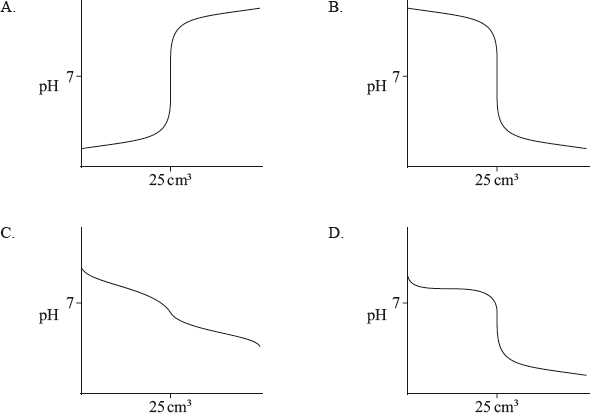
Which graph would be obtained by adding \({\text{0.10 mol}}\,{\text{d}}{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}{\text{HCl(aq)}}\) to \({\text{25 c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}}\) of \({\text{0.10 mol}}\,{\text{d}}{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}{\text{NaOH(aq)}}\)?
The \({\text{p}}{K_{\text{b}}}\) value of ammonia is 4.75 at 298 K. What is the \({\text{p}}{K_{\text{a}}}\) value of the ammonium ion?
A. \(\frac{{{\text{1}}{{\text{0}}^{ - 14}}}}{{{\text{4.75}}}}\)
B. \(\frac{{{\text{14.00}}}}{{{\text{4.75}}}}\)
C. \(14.00 - 4.75\)
D. \(\frac{{{\text{1}}{{\text{0}}^{ - 14}}}}{{{\text{1}}{{\text{0}}^{ - 4.75}}}}\)
Which compound will produce an aqueous solution which has a pH greater than 7?
A. \({\text{CuS}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\)
B. \({\text{FeC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}\)
C. \({\text{N}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\)
D. \({\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}{\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\)
Which mixture is a buffer solution?
A. 25 cm3 of 0.10 mol dm-3 NH3 (aq) and 50 cm3 of 0.10 mol dm-3 HCl (aq)
B. 50 cm3 of 0.10 mol dm-3 NH3 (aq) and 25 cm3 of 0.10 mol dm-3 HCl (aq)
C. 25 cm3 of 0.10 mol dm-3 NaOH (aq) and 25 cm3 of 0.10 mol dm-3 HCl (aq)
D. 50 cm3 of 0.10 mol dm-3 NaOH (aq) and 25 cm3 of 0.10 mol dm-3 HCl (aq)
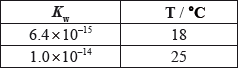
The values of \({K_{\text{w}}}\), the ionic product constant of water, are:
Which statements are correct?
I. The \({\text{[O}}{{\text{H}}^ - }{\text{]}}\) in water is less than the \({\text{[}}{{\text{H}}^ + }{\text{]}}\) at 18 °C.
II. The ionization of water is an endothermic process.
III. The pH of water is lower at 25 °C than at 18 °C.
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
What is the approximate pH of a \({\text{0.01 mol}}\,{\text{d}}{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}\) ammonia solution?
A. 2
B. More than 2 but less than 7
C. More than 7 but less than 12
D. 12
What is the order of increasing acidity?
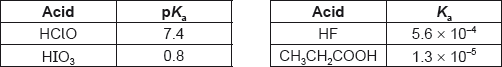
A. HClO < CH3CH2COOH < HF < HIO3
B. HClO < HF < CH3CH2COOH < HIO3
C. HIO3 < HF < CH3CH2COOH < HClO
D. HIO3 < CH3CH2COOH < HF < HClO
What is the order of increasing acidity of the following acids?
A. chloroethanoic < ethanoic < hydrogen fluoride < hydrogen cyanide
B. ethanoic < chloroethanoic < hydrogen fluoride < hydrogen cyanide
C. chloroethanoic < ethanoic < hydrogen cyanide < hydrogen fluoride
D. hydrogen cyanide < ethanoic < hydrogen fluoride < chloroethanoic
Which indicator is appropriate for the acid-base titration shown below?
A. Thymol blue (pKa = 1.5)
B. Methyl orange (pKa = 3.7)
C. Bromophenol blue (pKa = 4.2)
D. Phenolphthalein (pKa = 9.6)
A buffer is produced by mixing 20.0 cm3 of 0.10 mol dm−3 ethanoic acid, CH3COOH(aq), with 0.10 mol dm−3 sodium hydroxide, NaOH(aq).
What is the volume of NaOH required and the pH of the buffer?
The forward reaction of this equilibrium is endothermic.
\[{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O(l)}} \rightleftharpoons {{\text{H}}^{\text{ + }}}{\text{(aq)}} + {\text{O}}{{\text{H}}^ - }{\text{(aq) }} {K_w} = 1.0 \times {10^{ - 14}}{\text{ at 25 }}^\circ {\text{C}}\]
What is correct about water at 50 °C?
A. \({\text{[}}{{\text{H}}^{\text{ + }}}{\text{]}} > {\text{[O}}{{\text{H}}^ - }{\text{]}}\)
B. \({\text{[}}{{\text{H}}^ + }{\text{]}} < {\text{[O}}{{\text{H}}^ - }{\text{]}}\)
C. \({\text{pH}} < {\text{7.0}}\)
D. \({\text{pH}} = {\text{7.0}}\)
Which indicator would be the most appropriate for titrating aqueous ethylamine, \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\), with nitric acid, \({\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\)?
A. Bromophenol blue \({\text{(p}}{K_{\text{a}}} = {\text{ }}4{\text{.}}1)\)
B. Bromothymol blue \({\text{(p}}{K_{\text{a}}} = {\text{ }}7{\text{.}}3)\)
C. Phenol red \({\text{(p}}{K_{\text{a}}} = {\text{ }}8{\text{.}}0)\)
D. Thymolphthalein \({\text{(p}}{K_{\text{a}}} = {\text{ }}10{\text{.}}0)\)
Which mixture of solutions can be used to prepare a buffer solution?
A. \({\text{50.0 c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}}{\text{ 0.100 mol}}\,{\text{d}}{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}{\text{ HCl}}\) and \({\text{100.0 c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}}{\text{ 0.100 mol}}\,{\text{d}}{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}{\text{ N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\)
B. \({\text{50.0 c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}}{\text{ 0.100 mol}}\,{\text{d}}{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}{\text{ HCl}}\) and \({\text{50.0 c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}}{\text{ 0.100 mol}}\,{\text{d}}{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}{\text{ N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}\)
C. \({\text{50.0 c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}}{\text{ 0.100 mol}}\,{\text{d}}{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}{\text{ HCl}}\) and \({\text{100.0 c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}}{\text{ 0.100 mol}}\,{\text{d}}{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}{\text{ N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}{\text{Cl}}\)
D. \({\text{50.0 c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}}{\text{ 0.100 mol}}\,{\text{d}}{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}{\text{ HCl}}\) and \({\text{50.0 c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}}{\text{ 0.100 mol}}\,{\text{d}}{{\text{m}}^{ - 3}}{\text{ N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{4}}}{\text{Cl}}\)
An equal amount of each of the following salts is added separately to the same volume of water.
Which salt will have the greatest effect on the pH of water?
A. \({\text{Al(N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{)}}_{\text{3}}}\)
B. \({\text{N}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\)
C. RbCl
D. KBr
Which compound forms an acidic solution when dissolved in water?
A. \({\text{FeC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{3}}}\)
B. \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\)
C. \({\text{NaN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\)
D. \({\text{N}}{{\text{a}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\)
Which compounds can be mixed together as aqueous solutions of equal volume and concentration to form an acidic buffer solution?
A. Sodium hydrogensulfate and sulfuric acid
B. Sodium propanoate and propanoic acid
C. Ammonium chloride and ammonia solution
D. Sodium chloride and hydrochloric acid
Which statements about an acid–base indicator are correct?
I. It can be a weak acid.
II. It is a substance in which the conjugate acid/base pair are different colours.
III. It can be a weak base.
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
Which titration curve would occur when a weak acid is added to a strong base?